- Technical Information
- Internal Structure of Solenoid Diaphragm Valve
Internal Structure of Solenoid Diaphragm Valve
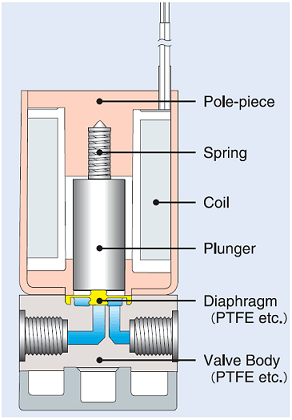
Takasago's solenoid diaphragm valve consists of two parts. One is the valve part, which opens and closes the flow path, and the other part is the actuator part, which operates the valve part. A membrane (diaphragm) inside the valve isolates these two parts from each other. The diaphragm prevents fluids from running inside the valve part (made of highly inert plastics such as PTFE and PEEK) from flowing into the actuator, mainly metal. This function of the diaphragm prevents fluids from corroding the actuator. Over the cycles of operations, metal specks of dust, etc., are generated from the actuator, and the diaphragm also prevents dust particles from mixing into fluids.
This structure is ideal for applications such as analytical and medical instruments' sampling devices, which do not tolerate impurities. It is also suitable for handling acids and chemicals which corrode metals. A valve with this kind of structure is also called a "(chemically) inert valve."
Note: Details such as specifications, etc., may be changed without notice.
2-way Diaphragm Valve Internal Structure

3-way Diaphragm Valve Internal Structure

Note: Details such as specifications, etc., may be changed without notice.
Please feel free to contact us for more information about the technical details of the Internal Structure of Solenoid Diaphragm Valve.
If you cannot find a suitable solenoid diaphragm valve, please feel free to send us an inquiry, and we can offer extensive customization options to meet your specifications.
